Review Article - Clinical Practice (2022) Volume 19, Issue 3
Role of NRG1 coalescence for treatment of lung cancer in patients
- Corresponding Author:
- Shahbal Shahbal
Department of Psychology-International Islamic University, Pakistan
E-mail: syedshahabal@gmail.com
Received: 20 April, 2022, Manuscript No. fmcp-22-61321, Editor assigned: 25 April, 2022, PreQC No. fmcp-22-61321, Reviewed: 16 May, 2022, QC No. fmcp-22-61321, Revised: 20 May, 2022, Manuscript No. fmcp-22-61321, Published: 25 May, 2022, DOI. 10.37532/fmcp.2022.19(3).1937-1941
Abstract
Gene-targeted treatments for lung cancer have significantly increased survival rates when compared to conventional chemotherapy. In both Europe and the United States, researchers are looking into the therapeutic potential of a gene fusion called Neuregulin 1 (NRG1). The purpose of this review is to highlight the importance of this novel fusion in the treatment of lung cancer and the most recent achievements in this field. In a broad spectrum of cancers, oncogenic gene fusions originate from structural DNA rearrangements that promote uncontrolled cell proliferation. The genes of crossbreeds, as a result, drugs to inhibit cell growth and proliferation have been created. Lung cancer therapy is increasingly focusing on oncogene fusions such as ALK, RET, NTRK, and ROS1, among others. Many diseases have been linked to NRG gene fusions, which have been linked to a variety of solid tumors (including kidney and pancreatic cancer, breast and colorectal cancer, and lung cancer). As has been the case for decades, oncology treatment will continue to evolve, moving from a focus on the disease’s genesis to a more genetically-based approach. In addition to improving survival rates, the increased availability of these drugs has sparked a renewed interest in finding new therapies.
Keywords
Multiplex Technique, NRG gene, Molecular indicators, Oncogenic gene fusions.
Introduction
Medical oncology’s diagnostic and treatment options are becoming more personalized, and that trend will only accelerate. A patient’s prognosis, responsiveness to therapy, and survival will be aided by the presence or absence of particular genetic anomalies. A slew of pharmaceuticals has been given FDA targeted therapy approval in the previous ten years. Many gene abnormalities may be targeted, including EGFR, BRAF, ROS, RET; KRASg12c; NTRK; PD1; IDH1/2, and FGFR. As a result of this, questions have been raised concerning the use of other molecular indicators, as well as blood tests, such as liquid biopsies. When DNA reorganization results in uncontrolled activity, oncogenic gene fusions occur as supported by the findings of Muscarella, et al. [1].
The 8p12 region of chromosome 8 may contain the NRG1 gene. One of the growth factors produced by this gene is Neuregulin 1 (NRG1). When the Ebb/HER receptor complex interacts with NRG1’s tyrosine kinase ErbB3, it activates downstream signaling pathways that result in cell proliferation. There may be EGF-like domains in NRG1. As a result, drugs that specifically target NRG1 are now being researched [2].
Expression of NRG1
KRAS and ALK have known proto-oncogenes that may generate NRG1 rearrangements. Cancer patients with various mutations may now be treated with TKI drugs, which target a wide range of different receptors and genetic abnormalities in the same tumor. A wide variety of malignancies, not only those with singlemutation receptors, may benefit from the use of TKIs [3].
The expression of NRG1 is adaptable in nonneoplastic conditions. In-depth discussions have been held on the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and neurological systems. When cardiomyocytes are injured or overworked, the expression of NRG1 increases, resulting in the activation of fibroblasts and macrophages, which may contribute to the development of heart failure. To provide an example, researchers have shown that NRG1 may help to enhance cardiac function in many heart failure models, and the compound is currently being investigated in atrial fibrillation in addition to other cardiac disorders, such as Hirschsprung’s disease [4].
Even if the NRG1 gene is not present in the nervous system, Alzheimer’s disease may still arise. CSF NRG1 expression has been discovered to have a negative association with cognition in Alzheimer’s disease patients, according to Mouton-Liger, et al. [5] Cortical stroke treatment has been demonstrated to have a protective effect on persons with schizophrenia who have a positive association between cognition and schizophrenia [6].
NRG1 reports in lung cancer
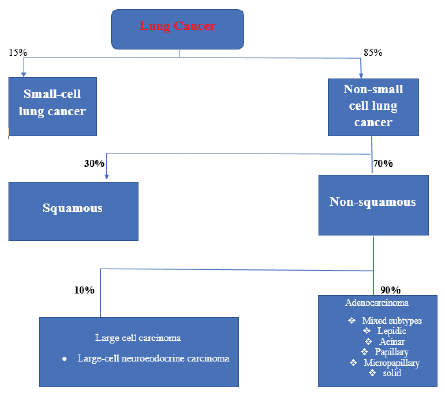
More than a dozen malignancies have been linked to alterations in NRG1. Tumors were found in 0.2 percent of the 21,858 tissue samples studied by Janna and her colleagues. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) was the most seen kind of lung cancer (NSCLC). Besides prostate and colorectal cancer, there have been reports of NRG1 fusions in various forms of cancer, including digestive tumors, squamous cell carcinoma, and breast cancer, other tumor types that have been linked to NRG1 fusions include prostate and colorectal cancers, as well as squamous cell carcinoma (sarcoma). Clinically, these tumors can be treated. NSCLC cancer cases, specifical adenocarcinomas, were found to have NRG1 rearrangements in 0.14 percent (3/2079) of the cases, while pancreatic adenocarcinomas had NRG1 rearrangements in 0.13 percent (1/791) of the cases, and breast cancer cases had NRG1 rearrangements in 0.04 percent (1/2703) of the cases. NRG1 fusions were found in 11% of patients having wild-type KRAS of lung cancer, which is a significant finding (4 of 36). [4/18/36] Researchers Fernandez-Cuesta, et al. [6] suggested that among nonsmokers, Smokers are more likely to have NRG1 alterations than nonsmokers. NRG1 was found in four of the 15 IMA subtypes of lung adenocarcinoma after screening 102 tumors with no known oncogenic alterations (IMA) [7].
Patients with lung IMA NRG1+ received alemtuzumab, an anti-ERBB3 antibody, in an exploratory treatment study published in Cancer Research. Both patients were treated with the assumption that they had failed at least three previous rounds of treatment and needed a new approach as explored also by Laskin, et al. [8]. Without experiencing any unacceptable toxicity, a PFS of at least sixteen weeks was possible. Since NRG1 rearrangements are common in IMA patients, more research into novel treatment approaches, such as targeting HER2, is warranted, given the rarity and severity of this disease (FIGURE 1). According to many investigations, such as that conducted by Dhanasekaran, et al. [9] modifications to NRG1 result in both cell proliferation and apoptosis escape when certain mutations occur, whereas other mutations and protein fusions result in cell death. Scientists believe that both the overexpression and the downregulation of this mechanism might increase cellular proliferation in the body. In light of this hypothesis, more study is needed to establish whether tumor regression may be caused by both inhibiting this mechanism and eliminating the agonist. It is possible that identifying activating fusions of NRG1 may need some care, regardless of whether or not this is the answer.
■Diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer
For women with ERBB2-positive breast cancer, the cornerstone of treatment is a single session of targeted therapy. Trastuzumab resistance may be caused in Yang, et al. [10] studies by an increase in the expression of NRG1 in the cancer cells. Because this gene aberration may show not only another type of targetable receptor but also a modifiable receptor that may be utilized to prevent resistance to anti-HER2 therapy, researchers are more interested than ever in this gene aberration. Rearrangements of NRG1 in breast cancer are a poor prognostic factor [11].
When chemotherapy is used alone or in combination with surgery or radiation therapy, it is the more common type of lung cancer treatment. Relapsed or resistant patients may benefit from the use of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) to find the best therapeutic choice for them. Increasing NRG1 expression in tumor cells may counteract the toxic effects of chemotherapy, which might lead to treatment resistance. This study analyzed six patients with NRG1 gene fusions, five of whom were diagnosed with LMA and one with CRC, according to the authors, who all received afatinib for their treatment. Only one of the five patients who received therapy for lung cancer achieved a Complete Remission (CR), while four of the five had Partial Responses (PR) (SD). The CRC patient had an excellent prognosis. To participate in the research, most patients had previously tried and failed many other treatments before being accepted. This case continuity suggests that NRG1 inhibitors may be a chance for those who have tried a variety of treatments. According to the study’s authors such as Wang, et al. [12], afatinib was used to treat three of 47 individuals with NGR1 rearrangement. Then there is Jones, too. Genome sequencing in all three cases showed a wild-type KRAS gene. NRG1 was discovered in gene fusions with wild-type KRAS in KRAS malignancies. Because their tumors were NRG1 fusion-positive, both patients responded to afatinib. These patients included one who had previously battled colon and stomach cancers, as well as one who had previously dealt with cancers of the prostate and the urethra. As more studies come to light showing that the NRG1 mutation increases one’s risk of developing a wide range of malignancies, it may be used as a genetic marker in future liquid biopsy procedures. Overexpression of NRG1 and activation of a parallel pathway in HER2-positive breast cancer models as well as ALK-positive lung cancer models may explain resistance to NRG1-targeting medicines, according to their results. According to the study by Yang, et al. [10] 28.1 percent of the 502 gastric cancer samples analyzed (141 individuals) were positive for NRG1. High pathological stage and poor prognosis have been linked to NRG1 overexpression although these traits have not been proved to be associated with NRG1’s presence. Examples of aggressive cancer features include infiltrative tumor growth, lymph venous invasion, and brain invasion. Researchers in this study discovered that high levels of NRG1 expression were linked to poor clinical outcomes, which implies that drugs that specifically target NRG1 might be useful in the treatment of gastric cancer. The report of 25 French patients having IMA was published in a medical publication. One ROS1 rearrangement, 12 KRAS mutations, and one ALK rearrangement were the most prevalent mutations detected in 14 of the 25 IMAs (4 percent). Eleven of the pan-negative IMAs analyzed had NRG1 rearrangements. According to Zhou, et al. [13] rearrangement of the NRG1 gene was carried out on a Vietnamese woman, who was aged 61 and had never smoked. Before her current diagnosis, this woman had had neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiation treatment for breast cancer [14]. There are two main conclusions the authors have drawn. NRG1 FISH testing should be performed in people having pan-negative IMA, as well as patients of Asian descent are more likely to have NRG1 abnormalities than non-Asian patients with IMA as mention also by Munafo, et al. [15]. To conclude these findings, the study’s small sample size must be considered. In the Annals of Oncology, a two-case study was published. Patients with cholangiocarcinoma and lung cancer had their NRG1 rearrangements quite different from one another, however, the TKI afatinib was employed to treat both of them throughout their chemotherapies. Responses in both patients were statistically significant and sustained.
NRG studies about treatment
The eNRGy1 global multicenter registry just released new data. In the greatest retrospective study to date, the clinical and pathological qualities of lung cancer carrying patients with NRG1 rearrangements were studied, giving important information on diagnostic processes and therapy response rates for conventional therapies [16]. There were more NRG1 gene fusions found in non-metastatic people (71%) and those who had never smoked (57%) than in those who did (57 percent). At the very least, 57% of the population. Quantity (57 percent) RNA sequencing has a higher detection rate than DNA sequencing. Among patients with NRG1 rearrangements, the median PFS was 5.8 months for those patients who received chemotherapy (ORRs of 13% as well as 14%, respectively; while the median PFS of 4.0 months in those patients who received chemotherapy) as well as 3.6 months for those patients who acquire immunotherapy alone (ORR of 20%; median PFS of 3.6 months) (ORR 20 percent as well as PFS 3.6 months) [17]. Those Patients with metastatic disease who received afatinib showed good outcomes (ORR of 25% and PFS of 2.8 months) without regarding fusion partner. Reports by Laski, et al. [8] demonstrate a range of three to 36 months of response in a 19-case study of patients having various kinds of cancer. The NRG1 gene may be a useful prognostic factor, although current results are unclear, according to this research. More than half of the 115 surgical specimens evaluated by Pan and colleagues included NRG1 mutations, which may explain the association between NRG1 expression and Overall Survival (OS) and lower risk of recurrence after lung cancer resection. Patients with IMA who had NRG1 rearrangements may have additional driver mutations, such as KRAS and ALK fusions (10/16 NRG1 fusion-positive cases, and two additional instances, respectively, Shin et al. reported) [18]. A SLC3A2-NRG1 having rearrangement was combined with a worse Overall Survival rate in the study (OS).
A novel molecular subgroup has been identified by NRG1 mutations, paving the way for more research studies. The NRG1 gene was initially studied for its activity in cardiac, neurological, and gastrointestinal tissue development and response to injury and disease. Is considered an oncogene of enhancing significance, with therapeutic implications for personalized medicine. Future research will include more people and a broader range of tumors, including those that aren’t lung cancer, as we gain more insight into this mutation’s prevalence and impact [19].
Conclusion
The mechanisms of resistance for this combination regimen will need more investigation. The development of medications for rare illnesses is difficult, but evaluating pharmaceuticals that have already been approved for other uses is an option worth considering. Individualized treatment choices for lung cancer include expanding the use of multiple techniques that can identify a variety of druggable gene fusions. Considering the prevalence of NRG1 fusions in cancer patients, it is crucial to look for novel drugs that may have significant therapeutic benefits.
Conflict of interest
None.
References
- Muscarella LA, Rossi A. NRG1: A cinderella fusion in lung cancer? Lung Cancer Manag. 6, 121-123 (2017). [Goolgle Scholar] [Crossref]
- Trombetta D, Rossi A, Fabrizio FP, et al. NRG1-ErbB lost in translation: A new paradigm for lung cancer? Curr Med Chem. 24, 4213-4228 (2017). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Luraghi P, Bigatto V, Cipriano E, et al. A molecularly annotated model of patient-derived colon cancer stem-like cells to assess genetic and non-genetic mechanisms of resistance to anti-EGFR therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 24, 807-820 (2018).[Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Muscarella LA, Trombetta D, Fabrizio FP, et al. ALK and NRG1 fusions coexist in a patient with signet ring cell lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 12, e161-e163 (2017). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Mouton-Liger F, Dumurgier J, Cognat E, et al. CSF levels of the BACE1 substrate NRG1 correlate with cognition in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res Ther. 12, 1-10 (2020). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Fernandez-Cuesta L, Thomas RK. Molecular pathways: Targeting NRG1 fusions in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21, 1989-1994 (2015). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Budi NYP, Sethi R, Fauzi AR, et al. NRG1 variant effects in patients with Hirschsprung disease. BMC Pediatr. 18, 1-9 (2018). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Laskin J, Liu S, Tolba K, et al. NRG1 fusion-driven tumors: Biology, detection, and the therapeutic role of afatinib and other ErbB-targeting agents. Ann Oncol. 31, 1693-1703 (2020). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Dhanasekaran SM, Balbin OA, Chen G, et al. Transcriptome meta-analysis of lung cancer reveals recurrent aberrations in NRG1 and Hippo pathway genes. Nat Commun. 5, 5893 (2014). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Yang L, Li Y, Shen E, et al. NRG1-dependent activation of HER3 induces primary resistance to trastuzumab in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 51, 1553-1562 (2017). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Dugaucquier L, Feyen E, Mateiu L, et al. The role of endothelial autocrine NRG1/ERBB4 signaling in cardiac remodeling. Am J Physiol Circ Physiol. 319, H443-H455 (2020). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Wang Y, Ning Z, Zhou X, et al. Neuregulin1 acts as a suppressor in human lung adenocarcinoma via AKT and ERK1/2 pathway. J Thorac Dis. 10, 3166-3179 (2018). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Zhou X, Wang Z, Huang B, et al. Regulation of the NRG1/ErbB4 pathway in the intrinsic cardiac nervous system is a potential treatment for atrial fibrillation. Front Physiol. 9, 1082 (2018). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Xia D, Le LP, Iafrate AJ, et al. KIF13B-NRG1 gene fusion and KRAS amplification in a case of natural progression of lung cancer. Int J Surg Pathol. 25, 238-240 (2016).[Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Munafo MR, Thiselton DL, Clark T, et al. Association of the NRG1 gene and schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry. 11, 539-546 (2006). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Navarro-Gonzalez C, Huerga-Gomez A, Fazzari P. Nrg1 intracellular signaling is neuroprotective upon stroke. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2019, 1-15 (2019). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Rajasekaran A, Shivakumar V, Kalmady SV, et al. Impact of NRG1 HapICE gene variants on digit ratio and dermatoglyphic measures in schizophrenia. Asian J Psychiatry. 54, 102363 (2020).[Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Shin DH, Jo JY, Han JY. Dual Targeting of ERBB2/ERBB3 for the treatment of SLC3A2-NRG1-mediated lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 17, 2024-2033 (2018). [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Dimou A, Camidge DR. Detection of NRG1 fusions in solid tumors: Rare gold? Clin. Cancer Res. 25, 4865-4867 (2019).[Google Scholar] [Crossref]