Research Article - Clinical Practice (2017) Volume 14, Issue 3
GRACE: Geriatric patients tReated with Avastin in CRC multiple linEs
- Corresponding Author:
- M Albertsson
Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine
Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
E-mail: maria.albertsson@regionostergotland.se
Abstract
Continuous treatment with bevacizumab in elderly patients with mCRC: A phase IV prospective, open-label, single-arm trial to evaluate outcomes and safety with continuous bevacizumab treatment in combination with chemotherapy over disease progression.
Keywords
bevacizumab, capecitabine, elderly patients, colon cancer, rectal cancer
Treatment of elderly patients with mCRC
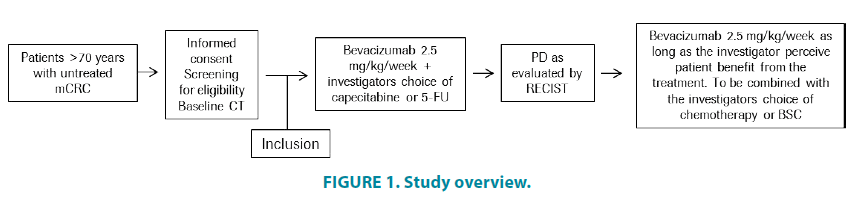
As with many cancer types, CRC is mainly diagnosed in elderly patients, with epidemiological data demonstrating that a majority of CRC patients are over 65 years of age, with a median age of around 70 years of age on diagnosis [1,2]. Despite this large and growing patient population, elderly patients are underrepresented in prospective randomized phase III trials; possibly due to strict eligibility criteria regarding performance status and comorbidities (FIGURE 1).
In the treatment of elderly patients, risks associated with old age need to be considered since these patients are more likely to present with an age-related decline in organ function and comorbidities [3,4]. The use of combination chemotherapy versus mono chemotherapy has been debated in the management of elderly mCRC patients. Most reports on combination chemotherapy show clinical improvements similar to those seen in younger patients but with an increased frequency of adverse events [5-9]. A retrospective analysis of the use of single-agent 5-FU chemotherapy in mCRC demonstrates that the benefits for older patients are similar to those seen among younger patients [10]. The Author’s research group has recently reported that low-dose capecitabine treatment can be an advantageous treatment option for elderly or frail mCRC patients [11].
Subgroup and pooled analyses from randomized trials, as well as data from observational studies, have suggested that the survival benefits of adding bevacizumab to first-line chemotherapy treatment are similar in elderly patients and the general population [12-17]. A phase III prospective trial on the addition of bevacizumab to capecitabine treatment in mCRC patients over the age of 70 was recently published [18-22]. This study demonstrated a significant improvement in the primary endpoint of progression-free survival for patients who received bevacizumab and capecitabine compared to those treated with capecitabine alone (9.1 vs. 5.1 months, HR 0.53, p<0.0001). In addition [22-26], the overall response rate was significantly improved (19% vs. 10 %, p=0.04). The total safety profile was in line with that reported in other studies of bevacizumab and capecitabine in mCRC [27-30].
More than half of patients diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer are over the age of 70 and are often not deemed fit enough to tolerate a combination chemotherapy treatment. For this patient group, a phase III trial recently showed that the combination of bevacizumab and mono-chemotherapy is an effective and tolerable treatment regimen [30].
Bevacizumab is an angiogenesis inhibitor with a separate mechanism of action to chemotherapy, implying that the development of chemotherapy resistance is not associated with the development of resistance to antiangiogenic treatment. Despite the development of chemotherapy resistance, data to support the beneficial effect of continuous treatment with bevacizumab has been published in preclinical and observational studies. The concept of continuous treatment was proved in a recent phase III prospective clinical trial which demonstrated increased overall survival in patients where bevacizumab was continued after first tumour progression [31].
There is a need to define effective and tolerable treatment strategies for the increasingly large group of elderly mCRC patients. This study aims to assess the feasibility of the new treatment modality of continuous bevacizumab treatment over progression in an elderly community-based patient population.
Study rationale
More than half of patients diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer are over the age of 70 and are often not deemed fit enough to tolerate a combination chemotherapy treatment. For this patient group, a phase III trial recently showed that the combination of bevacizumab and mono-chemotherapy is an effective and tolerable treatment regimen [30].
Bevacizumab is an angiogenesis inhibitor with a separate mechanism of action to chemotherapy, implying that the development of chemotherapy resistance is not associated with the development of resistance to antiangiogenic treatment. Despite the development of chemotherapy resistance, data to support the beneficial effect of continuous treatment with bevacizumab has been published in preclinical and observational studies. The concept of continuous treatment was proved in a recent phase III prospective clinical trial which demonstrated increased overall survival in patients where bevacizumab was continued after first tumour progression [31,32].
There is a need to define effective and tolerable treatment strategies for the increasingly large group of elderly mCRC patients. This study aims to assess the feasibility of the new treatment modality of continuous bevacizumab treatment over progression in an elderly community-based patient population.
Objectives
Primary objective
• To assess Overall Survival (OS) from time of inclusion
Secondary objectives
The secondary objectives are:
• To assess safety parameters in elderly patients receiving continuous bevacizumab treatment beyond progression.
• To assess total treatment duration as the time from the start of treatment at inclusion until the end of the final treatment.
• To assess treatment duration from first progression as the time from progression until the end of the final treatment.
• To assess progression-free survival as the time from inclusion until first progression or death.
• To assess patient-reported outcomes, including health-related quality of life, as measured by EORTC QLQ-C29, across multiple lines of bevacizumab-containing regimens.
• To assess Overall Response Rate (ORR).
Exploratory objectives
• To investigate the correlation between biomarkers and outcomes of continuous bevacizumab treatment by collecting and analysing tumour samples and serial blood samples.
Study design
This is a phase IV, prospective, open-label, multicentre study of patients over 70 years of age with previously untreated metastatic CRC. A total of 100 patients will be recruited.
Patients included in the study will be treated with bevacizumab and capecitabine or 5-FU. Patients will remain on first-line treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. If toxicities due to capecitabine or 5-FU require their respective discontinuation patients will continue to be treated with bevacizumab.
Assessments during the study are described in the schedule of assessments. Tumour status will be assessed at regular intervals according to clinical practice. After first progression is established according to RECIST 1.1 criteria, patients fit for second-line treatment will remain on bevacizumab plus the investigator’s choice of chemotherapy or Best Supportive Care (BSC) for as long as the investigator considers that the treatment is beneficial.
Study population
Patient inclusion criteria
• Patients with a histologically confirmed diagnosis of adenocarcinoma of the colon or rectum.
• Age ≥ 70.
• Measurable disease according to RECIST criteria.
• ECOG/WHO Performance Status 0-2
• Life expectancy of more than 3 months but not considered optimal candidate for treatment with combination chemotherapy with oxaliplatin or irinotecan
• Adequate haematological, renal and liver function;
• haemoglobin >90 g/L (may be transfused to maintain or exceed this level)
• absolute neutrophil count ≥ 1,5 × 109/L
• platelets ≥ 100 × 109/L
• bilirubin ≤ 1.5 × ULN, ALAT ≤ 2.5 × ULN (<5 × ULN if liver metastases)
• creatinine ≤ 1.5 × ULN
• PK ≤ 1.5
• APTT <1.5 ULN
• Urine dipstick of proteinuria <2 + (patients discovered to have ≥ 2 + proteinuria on dipstick urinalysis at baseline, should undergo a 24-hour urine collection and must demonstrate ≤ 1 g of albumin/24 h)
• Tumour tissue available for biomarker analysis.
• Written informed consent signed by the patient to the clinical study and translational research according to ICH/GCP and the local regulations
Patient exclusion criteria
• Previous treatment with chemotherapy within the past 6 months.
• Surgical procedure or significant traumatic injury within 28 days prior to first study treatment, or anticipated need for major surgical procedure during the course of the study.
• Clinically significant (i.e. active) cardiovascular disease, for example cerebrovascular accidents ≤ 6 months prior to study enrolment, myocardial infarction ≤ 6 months prior to study enrolment, unstable angina, New York Heart Association Grade II or major Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) (see Appendix 1), or serious cardiac arrhythmia either unmedicated or with the potential to interfere with protocol treatment.
• Other malignancy within 5 years except for carcinoma in situ of the cervix, basal or squamous cell skin cancer, localized prostate cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ treated with curative intent.
• Serious non-healing wound or ulcer.
• Evidence of bleeding diathesis or coagulopathy.
• International Normalised Ratio (INR)>1.5 and activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) <1.5 × ULN within 7 days prior to study enrolment for patients not receiving anticoagulants. The use of full oral or parenteral anticoagulants is permitted as long as the INR or aPTT is within therapeutic limits according to the medical standard of the enrolling institution and the patient has been on a stable dose of anticoagulants for at least two weeks prior to the first study treatment.
• Uncontrolled hypertension despite pharmacological antihypertensive treatment.
• Prior history of gastrointestinal perforation or abscess
• Significant vascular disease (e.g. aortic aneurysm requiring surgical repair or arterial thrombosis within 6 months of the start of study treatment). Any previous venous thromboembolism>NCI CTCAE Grade 3.
• Ongoing treatment with aspirin (>325 mg/day) or other medications known to predispose to gastrointestinal ulceration.
• Known hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients of any of the study drugs.
• Any other serious or uncontrolled illness or treatment with a medicinal product that in the opinion of the investigator makes it undesirable for the patient to enter the trial.
Patient enrolment
All patients must provide written Informed Consent before any study-specific assessment is performed.
Screening assessments should occur within 28 days of the first bevacizumab infusion and patients not meeting the eligibility criteria will not be enrolled into the study. Once the patient’s eligibility has been confirmed, the enrolment will occur and a patient ID number will be allocated to the patient via the electronic CRF (eCRF) website.
Tumour measurement
Tumours will be measured using a CT scan and assessed based on RECIST 1.1 criteria [26], with assessments performed by the same individual where possible. For patients with multiple measurable lesions up to 5 lesions per organ should be identified, recorded and measured as target lesions within 28 days prior to the start of treatment. A sum of the Longest Diameter (LD) for all targeted lesions will be calculated and reported as the baseline sum LD to be used as a reference for the characterization of tumour response. All other lesions should be identified as non-target lesions and recorded at baseline and described over time but without the need for measurement.
Where there is suspicion of progression before the next scheduled assessment, an unscheduled tumour assessment should be performed. If a patient misses a scheduled tumour evaluation or the evaluation is prevented by technical errors, the patient may continue treatment until the next scheduled assessment unless signs of clinical disease progression are presented.
Other clinical assessments
• Demographics and medical history – including age, gender and current diseases.
• Information on cancer and treatment history – date of diagnosis as recorded on the Pathological Anatomical Diagnosis (PAD).
• Concurrent disease – diseases potentially altering the risk/benefit ratio, such as significant cardiovascular disease, should be investigated for and recorded.
• Physical examination and vital signs – including height, weight, pulse, blood pressure.
• ECOG Performance Status – (See Appendix 5).
• ECG – will be recorded according to institutional standard and recorded as normal, abnormal clinically significant or abnormal clinically insignificant.
• PRO measures - EORTC QLQ-C29 (see Appendix 2), should be performed prior to the completion of other study assessments.
Laboratory assessments
• Haematology – including haemoglobin, platelet count, leukocytes and absolute neutrophil count. Local laboratory will perform the analyses and provide their reference ranges.
• Blood chemistry – including sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, albumin, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, ALAT, creatinine, CEA.
• Urinalysis – urine dipstick is sufficient as long as the protein result is <2+. If urine dipstick shows ≥ 2, a 24 h, urine collection should be performed (see also Appendix 3) for instructions for handling of proteinuria.
• Coagulation tests – aPTT and INR.
Assessment of biomarkers
Samples will be collected for biomarker analyses from all patients with the aim of identifying tumour biomarkers related to treatment efficacy and safety of bevacizumab treatment in elderly patients.
A formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sample from the time of diagnosis will be collected during the screening phase and sent to University Hospital Linköping.
Statistical considerations and analytical plan
The study is designed as a phase IV, prospective, open-label, single-arm trial to evaluate outcomes and safety of continuous bevacizumab treatment in combination with chemotherapy over disease progression in elderly mCRC patients.
Sample size calculation
It is planned to include 100 patients in the study. With an estimated accrual time of 36 months, a follow up time of 24 months and assumptions of OS being exponentially distributed, a one-sided Brookmeyer-Crowley test, an alpha level of 10%, a power of 80% and a median OS of 22 months in the study patients versus 15.7 months observed in patients on chemotherapy only; sample size was calculated to 89 patients. To allow for a dropout rate of 10%, it is planned to enroll 100 patients. It is estimated that approximately 35% of patients will continue treatment for mCRC after progression and will thus be candidates for continued bevacizumab treatment (based on data from the AVEX study [30].
Analysis populations
The Intention to Treat (ITT) population includes all consenting patients enrolled in the study. The safety population comprises all patients who received at least one dose of study medication. The per-protocol population excludes all patients with major protocol violations.
The data from the ITT population will be presented descriptively and used for primary efficacy analysis. The efficacy analysis will be repeated using the per-protocol population to confirm the overall study results. All safety analyses will be based on the safety population.
Data management
Data management in accordance with ICH guidelines, CRO standard operating procedures and good clinical, scientific and data management principles.
Ethical considerations
The study protocol was approved by the Regional Ethical Board in Linköping, Sweden (reference number: 2016/429-32) in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki, 1964 and as amended by the WMA General Assembly, Tokyo, 1975. All patients participating in this study have provided written informed consent.
Preliminary results
So far, 29 patients have been screened (14 female and 15 male) and 20 patients are included in the study. No unexpected side effects or complications have been recorded. Eleven patients are alive, two with no evidence of disease (NED) post-surgery.
Discussion
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most commonly diagnosed malignancy with approximately 1.4 million cases diagnosed per year [37]. In Sweden, 4,117 men and 3,723 women were diagnosed in 2012 [38]. Patients presenting with localised disease can often undergo surgical resection of the primary tumour and local lymph nodes, leading to cure in about 50% of the patients. However, approximately half of the patients will eventually develop metastatic disease and approximately 25% of patients present with metastases at the time of diagnosis [33].
The most common site for metastases in CRC is the liver, and treatment strategy in these patients is based on a number of variables that include patient performance status, tumour size, the number of metastases and their localization. The majority of patients with metastasized CRC (mCRC) are not considered candidates for surgical metastasectomy and the treatment goals in this group mainly consist of prolonging survival and time to progression and decreasing tumour burden and tumour-related symptoms. The medical treatment of these patients consists of chemotherapy in combination with biological targeted treatment.
Anti-angiogenic treatment with bevacizumab
Recent advances in molecular biology have resulted in an improved understanding of tumour cell-signalling processes and the intricate interplay with surrounding tissues involved in tumour growth. This has led to the development of targeted agents for the treatment of solid tumours, designed to interfere with those processes that are essential to tumour function. One successful approach involves inhibition of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). VEGF is a stimulator of new vessel proliferation and a potent survival factor for existing tumour vasculature. Without VEGF, recently formed microvasculature disintegrates and endothelial cells undergo apoptosis [34,35].
Many approaches have been developed to inhibit the VEGF pathway. The most successful of these is the development of the monoclonal humanized antibody bevacizumab (Avastin®), which prevents tumour angiogenesis by targeting circulating VEGF, preventing it from interacting with its receptors on the surface of endothelial cells.
Clinical data with bevacizumab in mCRC
In 2004, a large phase III trial (AVF2107g) was published demonstrating that bevacizumab improves the efficacy of fluoropyrimidinebased combination chemotherapy in previously untreated patients with mCRC [36]. This was the first trial to show that anti-angiogenic therapy could prolong survival. 813 patients were treated with irinotecan and 5-FU/LV (IFL regimen) and randomized to receive additional bevacizumab or placebo. Median overall survival, the primary endpoint, was improved from 15.6 to 20.3 months (HR: 0.54, p<0.0001). Progression-free survival was also improved (6.2 versus 10.6 months; HR: 0.66 p<0.001), as was response rate (35 versus 45%; p=0.004). The addition of bevacizumab to chemotherapy was generally well tolerated, with grade 3 hypertension (manageable using standard oral medication) clearly more frequent in the bevacizumab arm (10.9 versus 2.3%). Gastro-intestinal (GI) perforation, arterial thromboembolism and haemorrhaging were also identified as safety signals in the bevacizumabtreated patients; occurring at 1.6%, 3.3% and 3.1% respectively.
The addition of bevacizumab to 5-FU/LV or capecitabine alone or in combination with oxaliplatin has similarly demonstrated improved efficacy in the absence of unexpected toxicity [26-30]. Furthermore, safety and efficacy data on bevacizumab in combination with various chemotherapy regimens in CRC from the observational studies BRITE (n=1968) and FirstBEAT (n=1915) confirms the data from randomised trials in broader patient populations [33,31].
Treatment with bevacizumab in multiple lines
Preclinical studies have shown that VEGF is continually expressed during the tumour life cycle and that sustained VEGF inhibition achieves and maintains tumour regression [26,33]. The use of anti-angiogenic treatment, acting on genetically stable endothelial cells, should in principle induce less drug resistance compared to treatments directed at genetically unstable tumour cells (e.g. chemotherapeutic drugs). Consequently, continued antiangiogenic treatment can be clinically effective despite the development of chemotherapy resistance. In the large observational trials following the approval of bevacizumab for mCRC (BRiTE and ARIES), continued treatment with bevacizumab beyond first disease progression correlated with prolonged survival [34,35].
The concept of continuing bevacizumab treatment beyond progression in mCRC was prospectively tested in the TML trial (ML18147), in which mCRC patients receiving first-line treatment with combination chemotherapy and bevacizumab were randomised to cross over chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab at first progression. The study met its primary endpoint and showed that patients who received continuous bevacizumab treatment over progression had a significant prolonged overall survival compared to patients who stopped taking bevacizumab at progression (11.2 versus 9.8 months, HR 0.81, p=0.062). The study also showed that continuous bevacizumab treatment was associated with a significantly prolonged PFS (5.7 versus 4.1 months, HR 0.68, p<0.0001) and with a safety profile consistent with previously reported data in bevacizumab naïve patients [31].
Cancer is a disease of ageing. Over 60% of all diagnoses relate to people of 65 years of age or over. Despite this, the group is rarely included in research studies relating to new methods of treatment. The level of knowledge regarding how best to treat elderly and comorbid cancer patients is low and this often leads to them receiving inferior treatment [37-39].
Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer diagnosis. Its incidence increases with age, doubling every seventh year for patients over 50 years of age. There is a lack of information regarding the optimal treatment for colorectal cancer patients over 70 years of age, who often also suffer from other diseases, both with regard to effectiveness and quality of life. Intestinal cancer is roughly as common in men as in women, with approximately 4,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Around half of these relate to people 75 years of age or over.
Today, the relative 5-year survival rate for all cancer diagnoses is approximately 67%. This compares with 36% at the beginning of the 1970s. There is a gap in knowledge with regard to the optimal treatment for the aging patient.
The older a person is, the less relevant chronological age becomes from a medical perspective. In a group of 80-year-olds, one may find everything from entirely healthy and active individuals to gravely multiply ill people with enormous requirements for health and social care.
Here in Sweden, we have a unique opportunity to conduct clinical research into this patient group. We have a relatively prosperous aging population and a high-level of basic universal healthcare. We also have unique opportunities for following up our patients. This means that the results we produce can be generalized in a wider perspective.
In this study, we have found that compliance is high. Even in this group, there are patients that with neoadjuvant therapy are resectable and curable.
In this pilot material, we see Xx patients who live without signs of recurrence after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgery. We also see that there is a problem in initially prognosticating who these patients are likely to be. Some deteriorate rapidly and quickly die of their basic disease.
References
- Köhne et al. Chemotherapy in Elderly Patients with Colorectal Cancer. The Oncologist 13,390-402 (2008).
- Pallis, PapamichaelD, Audisio R, et al. EORTC Elderly Task Force experts’ opinion for the treatment of colon cancer in older patients. Cancer Treatment Rev 36,83-90 (2010).
- Sawhney R, Naeim A, Sehl M, et al. Physiologic Aspects of Aging: Impact on Cancer Management and Decision Making, Part II. The Cancer J 11,461-473 (2008).
- Sehl M, Sawhney R, Naeim A. Physiologic Aspects of Aging: Impact on Cancer Management and Decision Making, Part I. Cancer J 11(6),449-460 (2005).
- Goldberg RM, Isabelle TF, Bleiberg H, et al. Pooled analysis of safety and efficacy of oxaliplatin plus fluorouracil/leucovorin administered bimonthly in elderly patients with colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 24,4085-4091 (2006).
- Feliu J, Escudero P, Llosa F,et al. Capecitabine as fist-line treatment for patients older than 70 years with metastatic colorectal cancer: an oncpaz cooperative group study. J Clin Oncol 23(13),3104-3111 (2005).
- Twelves CJ, Butts CA, Cassidy J, et al. Capecitabine/Oxaliplatin, a Safe and Active First-Line Regimen for Older Patients Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Post Hoc Analysis of a Large Phase II Study. Clin Colorectal Cancer 5(2),101-107 (2005).
- Folprecht G, Seymour MT, Saltz L, et al. Irinotecan/fluorouracil combination in first-line therapy of older and younger patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: combined analysis of 2,691 patients in randomized controlled trials. J Clin Onc 26,1443-1451 (2008).
- Souglakos J, PallisA, Kakolyris S, et al. Combination of Irinotecan (CPT-11) plus 5-Fluorouracil and Leucovorin (FOLFIRI Regimen) as First Line Treatment for Elderly Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Phase II Trial. Oncology 69,384-390 (2005).
- Folprecht G, Cunningham D, Ross P, et al. Efficacy of 5-fluorouracilbased chemotherapy in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: a pooled analysis of clinical trials. Ann Oncol 15(9),1330-1338 (2004).
- Miger J, Holmqvist A, Sun XF, Albertsson M. Low-dose capecitabine (Xeloda) for treatment of gastrointestinal cancer. Med Oncol 31(3),870 (2014).
- Cassidy J, Saltz LB, Giantonio BJ, et al. Effect of bevacizumab in older patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: pooled analysis of four randomized studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(5),737-743 (2010).
- Kabbinavar FF, Hurwitz HI, Yi J, Sarkar S, Rosen O. Addition of bevacizumab to fluorouracil-based first line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: pooled analysis of cohorts of older patients from two randomized clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 27(2),199-205 (2009).
- Kozloff MF, Berlin J, Flynn PJ, et al. Clinical outcomes in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer receiving bevacizumab and chemotherapy: results from the BRiTE observational cohort study. Oncology 78,329-339 (2010).
- Kozloff M, Bekaii-Saab TS, Bendell JC, et al. Effectiveness of first or second line bevacizumab treatment in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer in ARIES, an observational cohort study. Am Doc Clin Oncol 29,3625 (2011).
- Price TJ, Zannino D, Wilson K,et al. Bevacizumab is equally effective and no more toxic in elderly patients with advanced colorectal cancer: a subgroup analysis of the AGTIG MAX trial: an international randomized controlled trial of capecitabine, bevacizumab and mitomycin C. Ann Oncol 23(6),1531-1536 (2012).
- Venderbosch S, Doornebal J, Teerenstra S,et al. Outcome of first line systemic treatment in elderly compared to younger patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective analysis of the CAIRO and CAIRO2 studies of the Dutch Colorectal Cancer Group. Acta Oncol 51(7),831-839 (2012).
- Cunningham D, Lang I, Marcuello E, et al. Bevacizumab plus capecitabine versus capecitabine alone in elderly patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer (AVEX): an open-label, randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 11,1077-1085 (2013).
- Bennouna J, Sastre J, Arnold D, et al. Continuation of bevacizumab after first progression in metastatic colorectal cancer (ML18147): a randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14(1),29-37 (2013).
- Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J of Cancer 45(2),228-247 (2009).
- Cutsem VE,Nordlinger B, Cervantes A, ESMO Guidelines Working Group.Advanced colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for treatment. Ann of Oncol 21 (Suppl 5): v93–v97 (2010).
- Gerber HP, Ferrara N. Pharmacology and pharmacodynamics of bevacizumab as monotherapy or in combination with cytotoxic therapy in preclinical studies. Cancer Res 65(3),671-680 (2005).
- Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM.Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumour growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23(5),1011-1027 (2005).
- Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25(4),581-611 (2004).
- Erber R, Vajkoczy P,Mohammad F,et al. Microtumor growth initiates angiogenic sprouting with simultaneous expression of VEGF, VEGF receptor 2 and angiopoietin 2. J Clin Invest 109(6),777-785 (2002).
- Kabbinavar FF, Schulz J, McCleod M, et al. Addition of bevacizumab to bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin in first-line metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 23,3697-3705 (2005).
- Tebbutt NC, Wilson K, Gebski VJ, et al. Capecitabine, Bevacizumab, and Mitomycin in First-Line Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Results of the Australasian Gastrointestinal Trials Group Randomized Phase III MAX Study. J Clin Oncol28(19),3191-3198 (2010).
- Hochster HS, Hart LL, Ramanathan RK, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Oxaliplatin and Fluoropyrimidine Regimens With or Without Bevacizumab As First-Line Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Results of the TREE Study. J Clin Oncol 26(21),3523-3529 (2008).
- Giantonio BJ, Catalano PJ, Meropol NJ, et al. Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFOX 4) for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer: results from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E3200. J Clin Oncol 25(12),1539-1544 (2007).
- Saltz LB, Clarke S, Díaz-Rubio E, et al. Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol 26,2013-2019 (2008).
- Kozloff M, Yood MU, Berlin J,et al. Clinical Outcomes Associated with Bevacizumab-Containing Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: The BRiTE Observational Cohort Study. Oncologist 14(9),862-870 (2009).
- Mesiano S, Ferrara N, Jaffe RB. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in ovarian cancer: inhibition of ascites formation by immunoneutralization. Am J Pathol 153(4),1249-1256 (1998).
- Klement G, Baruchel S, Rak J, et al. Continuous low-dose therapy with vinblastine and VEGF receptor-2 antibody induces sustained tumor regression without overt toxicity. J Clin Invest 105(8),R15–24 (2000).
- Grothey A, Sugrue MM, Purdie DM,et al. Bevacizumab beyond first progression is associated with prolonged overall survival in metastatic colorectal cancer: results from a large observational cohort study (BRiTE). J Clin Oncol 26(33),5326-5334 (2008).
- Cohn AL, Bekaii-Saab T, Bendell JC, et al. Clinical outcomes in bevacizumab (BV)-treated patients (pts) with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): results from ARIES observational cohort study (OCS) and confirmation of BRiTE data on BV beyond progression (BBP). J Clin Oncol 28,15s (suppl; abstr 3596) (2010).
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350(23),2335-2342 (2004).
- International agency for research on cancer. World Cancer Fact Sheet, Cancer research UK (2014).
- Swedish National Board of Health and Welfare. Cancer incidence in Sweden (2012).
- Van Cutsem E, Rivera F, Berry S,et al. Safety and efficacy of first-line bevacizumab with FOLFOX, XELOX, FOLFIRI and fluoropyrimidines in metastatic colorectal cancer: the BEAT study. Ann Oncol 20(11),1842-1847 (2009).