Review Article - Neuroscience and Psychiatry: Open Access (2022) Volume 5, Issue 3
The Future of Psychiatry as Clinical Neuroscience
Anthony Morris*, John Judt
University of Texas Health Science Center-- Houston USA
Received: 25-Jun-2022, Manuscript No. NPOA-22-52; Editor assigned: 27-Jun-2022, Pre-QC No. NPOA-22- 52(PQ); Reviewed: 11-Jul-2022, QC No. NPOA-22-52; Revised: 14-Jul- 2022, Manuscript No. NPOA -22- 52(R); Published: 21-Jul-2022, DOI: 10.37532/npoa.2022.5(3).57-60
Abstract
Psychiatry incorporates the appraisal, treatment, and counteraction of perplexing cerebrum problems, for example, despondency, bipolar confusion, tension issues, schizophrenia, formative issues (e.g., chemical imbalance), and neurodegenerative issues (e.g., Alzheimer dementia). Its center mission is to forestall and mitigate the pain and weakness brought about by these problems, which represent a significant piece of the worldwide weight of disease related handicap. Psychiatry is grounded in clinical neuroscience. Its center mission, presently and later on, is best served inside this setting since progresses in appraisal, treatment, and avoidance of cerebrum problems are probably going to start from investigations of etiology and pathophysiology situated in clinical and translational neuroscience. To guarantee its expansive general wellbeing pertinence later on, psychiatry should likewise span science and administration, guaranteeing that the individuals who need the advantages of its science are additionally its recipients. To do so actually, psychiatry as clinical neuroscience should reinforce its organizations with the disciplines of general wellbeing (counting the study of disease transmission), local area and conduct wellbeing science, and wellbeing financial matters. The creators present a Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) investigation of psychiatry and distinguish techniques for reinforcing its future and expanding its significance to general wellbeing and the remainder of medication. These procedures envelop new ways to deal with reinforcing the connection among psychiatry and nervous system science, supporting psychiatry’s central goal, underscoring early and supported multidisciplinary preparing (research and clinical), supporting the scholarly foundation, and redesigning and renegotiating emotional well-being administrations both for preventive intercession and practical persistent infection the executives. Psychiatry is the clinical specialty that looks to help (i.e., survey and treat) individuals and families living with complex mind problems including sorrow, bipolar turmoil, nervousness issues, schizophrenia, substance misuse problems, formative issues like chemical imbalance, and neurodegenerative issues like Alzheimer dementia. Generally, messes falling into the region of psychiatry have been those of obscure etiology, and, as analysts have learned etiology, a few problems, for example, focal sensory system issues have frequently moved to the territory of nervous system science. (Tertiary syphilis is a decent verifiable illustration of this shift.) Now, nonetheless, with the devices of current neuroscience, a more profound comprehension of causal pathways to major neuropsychiatric sickness is developing, hence delivering counterfeit the limit among psychiatry and nervous system science.
Keywords
AI ethics • Computational psychiatry • Consciousness • Ethics of consciousness • Mental disorders • Schizophrenia
Introduction
The computational psychiatry (CP, for example, profound learning, Bayesian models or support learning cross-over with techniques utilized in man-made brainpower. Albeit the techniques might be utilized for various points, they can raise comparable moral issues. Consequently contemplations from AI morals are likewise pertinent to CP. For example, calculations might create uncalled for results in the event that their preparation information are one-sided and the likelihood to gather and examinations individual information utilizing calculations raises issues of information possession and security Furthermore, numerous uses of AI are not reasonable, i.e., it is many times troublesome or difficult to decide why an AI framework yields a given result or who is responsible for the specific manner by which an AI framework works. [1] Such quick moral worries emerge for Utilizations of overall yet additionally for applications in mental medical services and CP specifically. Notwithstanding such quick worries, utilizations of AI can make ethically important extraordinary impacts. We utilize the expression “extraordinary impacts” extensively, in the feeling of tenacious changes that essentially influence human prosperity connected with certain parts of life and society in any event. These progressions need not be outrageous or extremist (in that frame of mind of groundbreaking nor need they on a very basic level change individual inclinations (in the feeling of extraordinary experience. Extraordinary impacts can in any case be expansive and significant, for example, by influencing the manner in which we think about independence and security, or by changing our approach to living through AI applications that saturate day to day existence. Also, effective uses of CP might change how we arrange and characterize mental problems which can have immediate and backhanded ramifications for the prosperity of impacted people. [2]Numerous psychological problems are described by upset cognizant experience. We will allude to such problems as issues of awareness. The term problem of cognizance is frequently held for scattered worldwide conditions of awareness, like inert attentiveness disorder insignificantly cognizant state, or unconsciousness. In these circumstances, attentiveness and mindfulness are reduced negligibly cognizant state), to some degree missing lethargic alertness or mutually missing. Here, we utilize the term from a more extensive perspective, which likewise covers problems including a disturbance of the
items or the construction or type of cognizant cycles including their spatiotemporal coherence, see Examples remember visualizations for psychosis freak time-and reluctance in significant burdensome issue depersonalization and decreolization in schizophrenia These circumstances need not oblige reduced degrees of alertness or mindfulness still they are described by disturbances of cognizant handling. Hence it will be valuable to allude to them as problems of cognizance in this paper. Fruitful utilizations of CP may consequently reshape how we think about issues of awareness and in this way likewise influence how we might interpret ‘typical’ cognizant encounters. [3] Changing our origination of typical and confused cognizant encounters could lessen or build up shame and increment or breaking point treatment choices. The possible extraordinary impacts of CP are accordingly ethically important. Specifically, they might diminish or build the prosperity of people experiencing mental problems. Consequently, they are likewise applicable according to the perspective of morals of awareness.
Case Presentation
Case 1
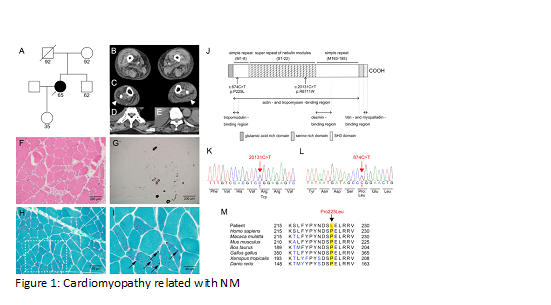
A 65-year-elderly person introduced seven days history of heart and respiratory disappointment. She was brought into the world at term without difficulties and introduced typical engine achievements in youth. There was no undeniable family background of neuromuscular infections. At 33 years old, she noted muscle decay transcendently found in the right lower limit. She step by step felt trouble in strolling because of right drop foot. She wanted an individual orthotics at 42 years old. On confirmation, she griped of dyspnea in a prostrate position and showed edema on reciprocal lower furthest points. [4] Her oxygen immersion was under 90% on room air, and blood vessel blood gas examination uncovered hypercapnia and hypoxemia with expanded alveolar-blood vessel angle. Then, at that point, she really wanted a ventilator because of her territory of CO2 narcosis. Fourteen days after confirmation, she was eluded to the neurological office to research a basic neuromuscular sickness prompting respiratory and cardiovascular breakdown Neurological assessments uncovered facial muscle shortcoming including slender high-curved sense of taste, and summed up however distal prevailing muscle shortcoming and decay. [5] Scoliosis was not noticed. Serious muscle shortcoming was seen in lower leg plantar flexion prevalently in the right side while gentle shortcoming was seen in furthest points (Figure 1).
Discussion
We report here a NEB-related NM patient giving gradually moderate distal myopathy respiratory and cardiovascular breakdown. She had a known missense variation of c.20131C > T and a clever variation of c.674C > T in NEB. Intriguingly, the novel missense variation, c.674C > T, is situated at the tropomodulin restricting site as known, tropomodulin keeps up with the slim fiber length by obstructing actin polymerization at the sharp end. This missense variation could foster NM through the misinteraction among cloud and tropomodulin like as past cases Heart disappointment is seldom seen in patients with NM particularly in NEBrelated NM. It tends to be made sense of by lower NEB articulation heart To date there have been just two patients with NEB-related NM introducing cardiovascular breakdown In the announced two NEB-related NM patients and our case, ECG and echocardiography were not demonstrative of any fundamental ischemic coronary illness or valvular sickness, which can be causative of cardiovascular breakdown. [6]One more conceivable reason for cardiovascular breakdown was pulmonale or cardiomyopathy related with NM. These three patients including the announced two cases exhibited respiratory disappointment notwithstanding cardiovascular breakdown demonstrating that pulmonale was related with their cardiovascular breakdown. Albeit the variation of c.20131C > T is normal in these patients with cardiovascular breakdown, the variation doesn’t influence the limiting of actin, proposing that the pathogenicity of the variation of c.20131C > T isn’t affirmed Indeed, the transporters of a solitary c.20131C > T variation show no unusual aggregate including myopathy or cardiovascular breakdown. Conversely, patients with cardiovascular association had another variation which can influence the limiting of tropomodulin (our case) or desman revealed two cases Previous in vivo/vitro concentrates on proposed that tropomodulin or desman may be connected with heart contribution. [7]Taken together, it is conceivable that the blend of the c.20131C > T variation and one more variation which can influence the association among cloud and tropomodulin or desmid is connected with create pulmonale in NEB-related NM.
Acknowledgement
The creators were upheld to a limited extent by P30 MH071944, Advanced Center for Interventions and Services Research for Late-Life Mood Disorders; NIH RR 024153 Clinical and Translational Science Institute (C.F.R., D.J.K.); and the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center gifts in geriatric psychiatry (C.F.R.); and Neuroscience (D.A.L.)
Conflict of Interest
The maker has no known disputes of charmed related with this paper.
References
- Thibaut F. Digital applications: the future in psychiatry. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 18, 123-123 (2016).
- Goldberg D. The future pattern of psychiatric provision in England. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin. 249, 123-127 (1999).
- Schnyder U. Future perspectives in psychotherapy. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin. 259, 123-128 (2009).
- Schnell K, Sabine C, Herpertz. Psychotherapy in psychiatry the current situation and future directions in Germany. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin. 261, 129-134 (2011).
- Devries MW. Neuroscience and the future of psychiatry. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 12, 638-639 (1999).
- Serretti A. The Present and Future of Precision Medicine in Psychiatry: Focus on Clinical Psychopharmacology of Antidepressants. Clin Psychopharmacology Neurosci. 16, 1-6 (2018).
- Thibaut F. Controversies in psychiatry. Dialogues Clin Neuro. 20, 152-152 (2018).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref