Image Article - Imaging in Medicine (2021) Volume 13, Issue 6
Polypoid lesions of the nasal cavity
- Corresponding Author:
- Oussama Amraoui
Department of ENT
Mohamed V University
Rabat
Morocco
E-mail: oussamra@gmail.com
Abstract
Case Description
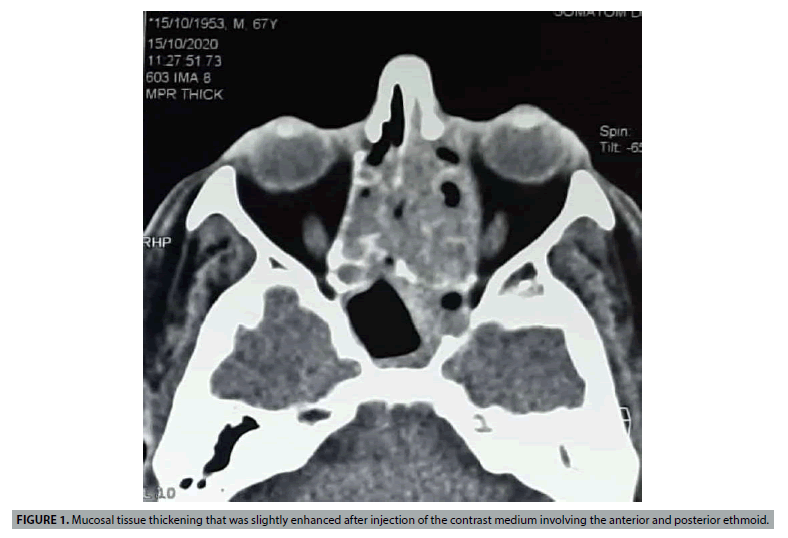
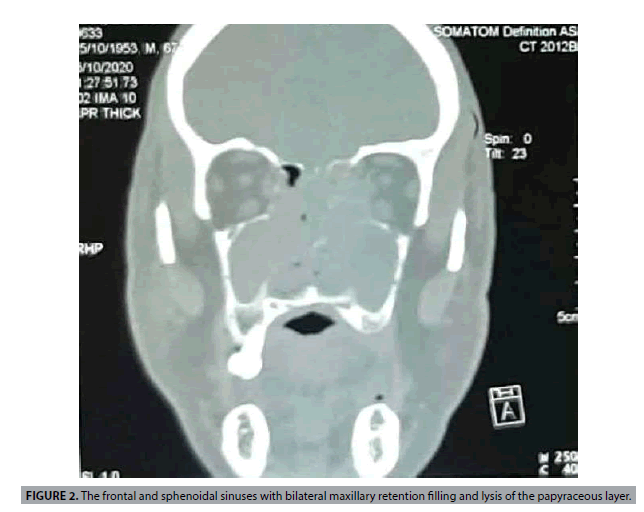
The patient was 67 years old, with no previous history, and was presented with a nasal obstruction that had been more marked on the left side for 6 months, associated with hyposmia without rhinorrhea, epistaxis, headache or ophthalmologic signs. The clinical examination did not reveal any deformity of the face and the lymph nodes were free. Nasal endoscopy showed a polypoid formation, budding in both nasal cavities, bleeding on contact, originating from the middle meatus and reaching the inferior turbinate. The CT scan showed a mucosal tissue thickening that was slightly enhanced after injection of the contrast medium involving the anterior and posterior ethmoid, the frontal and sphenoidal sinuses with bilateral maxillary retention filling and lysis of the papyraceous layer (FIGURES 1 AND 2).
Nasosinus polyposis appears to be the most likely diagnosis, especially in view of the bilateral nature of the lesions, the moderate enhancement and the minimal bone lysis. An inverted papilloma should also be considered, but the absence of a cerebriform appearance on the CT scan may eliminate the diagnosis. A biopsy was performed and found to be consistent with a small B-cell lymphoma showing an estimated Ki67 of 30% and CD 5 negative. The particularity of our case is the bilateral presentation of the tumor, the absence of adenopathies and the endonasal expression of this type of lymphoma which mainly affects the sinuses [1,2]. Moreover, on imaging, the lesion was not unilateral, the enhancement was moderate and the lysis was not frank, signs excluding malignancy. Radiochemotherapy is the standard treatment, but the prognosis is generally poor [3].
References
- Hatta C, Ogasawara H, Okita J et al. Non-Hodgkin's malignant lymphoma of the sinonasal tract--treatment outcome for 53 patients according to REAL classification. Auris Nasus Larynx. 28(1), 55-60 (2001).
- Abbondanzo SL, Wenig BM. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the sinonasal tract. A clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic study of 120 cases. Cancer. 75(6), 1281-1291 (1995).
- Quraishi MS, Bessell EM, Clark D, Jones NS, Bradley PJ. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the sinonasal tract. Laryngoscope. 110(9), 1489-1492 (2000).