Case Report - International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology (2021) Volume 16, Issue 6
Hemodialysis Induced Amyloid Arthropathy Presenting As Septic Arthritis : a case report
- *Corresponding Author:
- Soumaya Boussaid
Rheumatology Department, Rabta Hospital, Tunis, Tunisia
E-mail: soumayaboussaid@hotmail.com
Abstract
Dialysis-Related Amyloidosis (DRA) is a unique type of amyloidosis affecting patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis. It is defined by the deposition of the insoluble protein 2 microglobulin (B2M) in a variety of organs, but with high affinity for the osteo-articular system. The presentation may be subclinical and only apparent when a tissue biopsy is carried out. Gemellahaemolysans (G. haemolysans) is an opportunistic pathogen reported to infect immune-compromised patients and rarely observed in bone infections. We report the first case of septic arthritis due to G. haemolysans of a native knee and revealing an associated multi focal DRA.
Keywords
hemodialysis ● amyloidosis ● septic arthritis
Introduction
Dialysis-Related Amyloidosis (DRA) is a unique type of amyloidosis affecting patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis [1,2]. Amyloidosis is defined by the deposition of the insoluble protein β2 microglobulin (B2M) in a variety of organs however it has high affinity for type 1 collagen and predominantly affects the osteoarticular system [3]. The prevelence of DRA and associated arthropathy increases with the dialysis therapy duration [4]. This prevalence has substantially decreased with the development of new dialysis techniques that enhance the clearance of B2M as well as the development of kidney transplantation [5].
Gemellahaemolysans (G.haemolysans) is a Gram-positive coccus which forms part of the normal flora of the oro-pharynx and the upper respiratory tract found in approximately 30% of healthy adults and rarely causes clinically important infections [6]. It is an opportunistic pathogen reported to infect immunocompromised patients [7], but it could be observed in healthy people with no known diseases [8].
We report a rare case of amyloid arthropathy complicating DRA and revelead by a G.haemolysans septic arthritis.
Observation
A 50-year-old woman with renal failure secondary to type-2 diabetes undergoing dialysis since 15 years. She presented with three weeks acute knee pain with swelling and limited range of motion. Medical history showed several similar episodes of the same knee during the last five years and mechanical joint pain of both hips and shoulders.
In clinical examination we found subfebrile state, warm and swollen knee, floating patella, painful popliteal cyst and loss of knee extension.
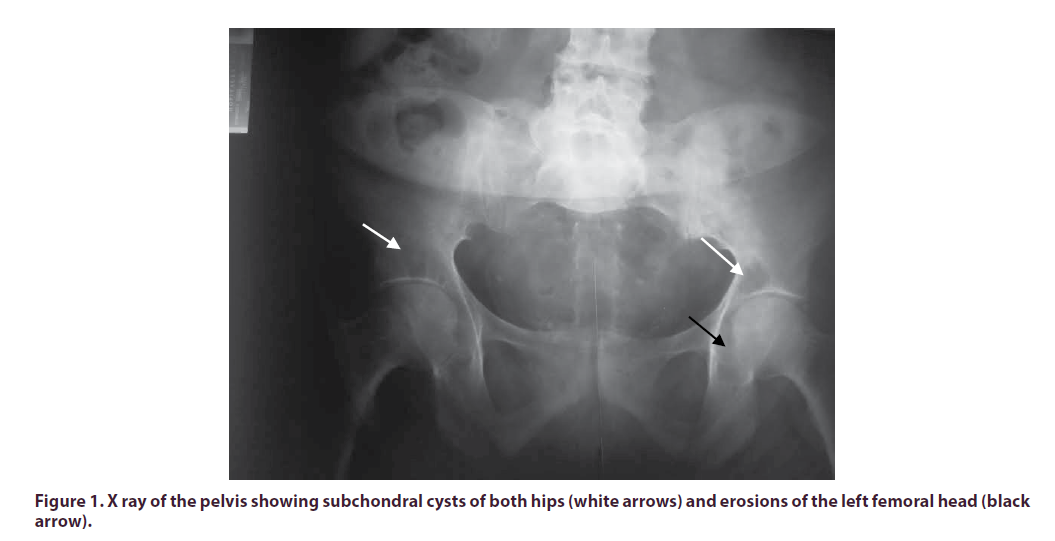
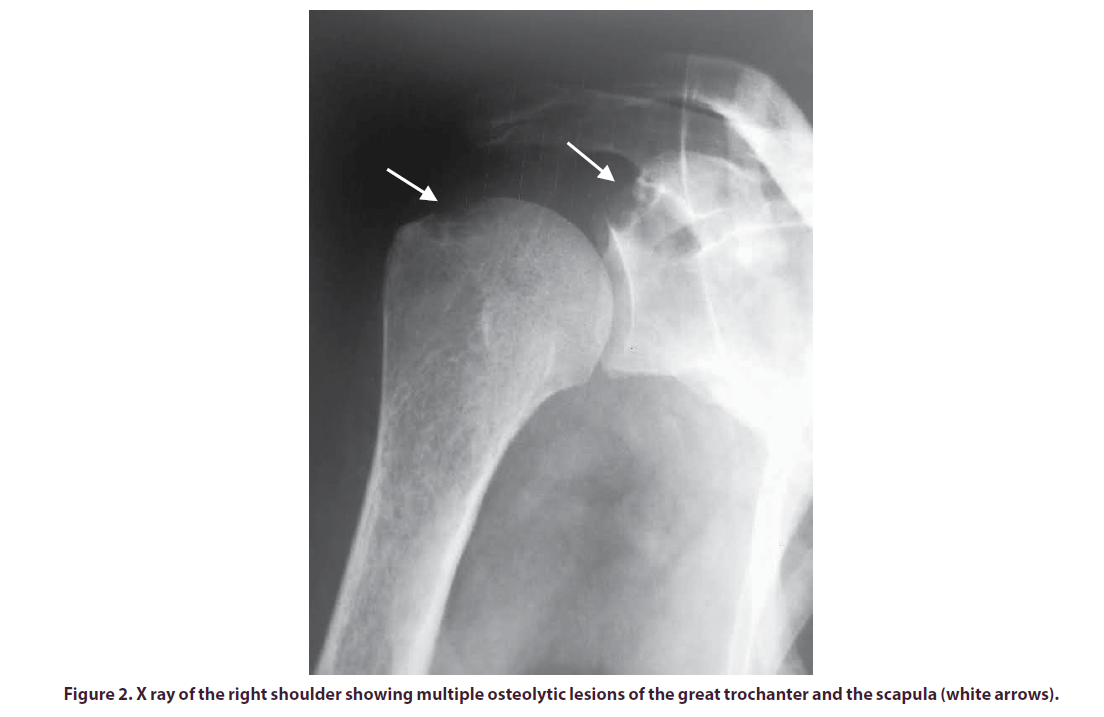
Laboratory findings revealed high level of C-reactive protein (56 mg/L), accelerated sedimentation rate (110 mm/h) and high white cell count. Blood cultures remained sterile and synovial fluid microbiological analysis and culture showed altered isolated G.haemolysans. No evidence of portal of entry for bacteremia was found. X-Ray imaging of the knee showed global tibiofemoral joint space narrowing and soft tissue swelling around the joint with no signs of destruction while x-ray imaging of the pelvis and shoulders showed multiple subchondral cysts of the pelvis, erosions of femoral heads (Figure 1) and right humeral head (Figure 2).
Synovial tissue biopsy analysis of the knee showed no signs of septic etiology, deposition of pink amorphous material stained orange with Congo red within the synovial tissue, and green birefringence under polarized light.
Other musculoskeletal disorders related to chronic renal failure treated by haemodialysis (hyperparathyroidism, crystal arthropathies, renal osteodystrophy) were not retained. Investigations for other rheumatic conditions were negative (normal anticyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor). Biopsy of salivary glands was practiced and didn’t show an amyloid localization.
Based on the radiological and histological data, a multifocal amyloid arthropathy was retained as a diagnosis.
The patient recevied adapted antibiotherapy for the septic arthritis with favorable outcomes. The fellow-up of two years showed good response of her arthralgia to analgesic and short term corticotherapy (0,1/mg/j of prednisone)
Discussion
The arthropathy related to DRA is erosive and progressive and commonly found in the shoulders, knees, and wrists [9]. It could mimic an inflammatory rheumatic condition particulary a seronegative rheumatoid arthritis [10-12].The patient has usually a polyarthralgia and the physical examination shows swollen joints with limited range of motion [13]. Mono or oligoarthritis is described and it is In some cases the clinical manifestation may be subtle, subclinical, and only apparent when a tissue biopsy is carried out [14]. Patients under hemodialysis had a higher incidence of septic arthritis comparing to controls with no renal failure which may be partly due to the higher rate of bloodstream infection in these patients [15]. In addition, these patients have many possible aseptic causes for arthritis making early diagnosis difficult [16]. Our patient had a septic arthritis due to an unusual bacteria, G. haemolysans.
G. haemolysans is very rarely involved in bone infections, even though probably under reported due to the variable time of growth and the difficulties in characterizing it with traditional methods [17]. To date, only four cases of spondylodiscitis [8,18,19] cases of total hip arthroplasty [17,6] one case of total knee arthroplasty infection [20] and one case of osteomyelitis of the clivus have been reported [21]. To the best of our knowledge this is the first case of septic arthritis due to G. haemolysans of a native knee and the first case of septic monoarthritis revealing an associated DRA. This association could be fortuitous and an hematological diffusion from a natural habitat of G. haemolysans is suspected since no evidence for a portal of entery was observed. Further studies are needed to investigate the incidence of septic arthritis in patients with long term hemodialysis and to establish guidelines for an early diagnosis of DRA of the musculoskeletal system.
Conclusion
Amyloidosis is a common complication of hemodialysis. However the clinical presentation is not specific. Multiple localizations are to be sought even in the absence of clinical signs.
References
- Koch KM. Dialysis-related amyloidosis. Kidney. Int. 41, 1416–1429 (1992).
- Kiss E, Keusch G, Zanetti Met al. Dialysis-related amyloidosis revisited. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 185, 1460–1467 (2005).
- Georgiades CS, Neyman EG, Barish MAet al. Amyloidosis:review and CT manifestations. Radiogr. Rev. Publ. Radiol. Soc. N. Am. Inc.24, 405–416 (2004).
- Van Ypersele de Strihou C. [Morphogenesis of beta 2m (A beta 2m) amyloiddeposits in dialysis patients]. Bull. Mem. Acad. R. Med.Belg. 155, 273–278 (2000).
- Schiffl H. Impact of advanced dialysis technology on the prevalence of dialysis-related amyloidosis in long-term maintenance dialysis patients. Hemodial. Int. Int. Symp. Home. Hemodial. 18, 136–141 (2014).
- Rose B, Jeer PJS, Spriggins AJ. Gemellahaemolysans Infection in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Case. Rep. Orthop .2012, e691703 (2012).
- La Scola B, Raoult D. Molecular Identification of Gemella Species from Three Patients with Endocarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36, 866–871 (1998).
- Martha B, Duong M, Buisson Met al. [Acute Gemellahaemolysans spondylodiscitis in an immunocompetent patient]. Presse. Medicale. Paris. Fr.32, 1273–1275 (2003).
- M’bappé P, Grateau G. Osteo-articular manifestations of amyloidosis. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 26, 459–475 (2012).
- Alpay N, Artim-Esen B, Kamali S, Gül A et al. Amyloid arthropathy mimicking seronegative rheumatoidarthritis in multiple myeloma: case reports and review of the literature. Amyloid. Int. J.Exp. Clin. Investig. Off. J. Int. Soc.Amyloidosis.16, 226–231 (2009).
- Katoh N, Tazawa K, Ishii W et al. Amyloidosis mimicking rheumatoid arthritis. Intern. Med. Tokyo. Jpn. 47, 1133–1138 (2008).
- Bowie D, Bardi M, Hemmati I. Amyloid Arthropathy: A Rare Mimic of Rheumatic Disease. J. Rheumatol. 46, 1540–1541 (2019).
- Masson E. Complications ostéoarticulaires des hémodialysés (hors ostéodystrophie rénale). EM. Consulte.(2021).
- Nguyen TX, Naqvi A, Thompson TLet al. Musculoskeletal Manifestations of Amyloidosis: A Focused Review. J. Surg. Orthop. Adv.27, 1–5 (2018).
- Zhang J, You X. Clinicalfeatures, riskfactors, and outcomes of septicarthritis in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 39, 3065–3069 (2020).
- Mathews CJ, Weston VC, Jones Aet al. Bacterial septicarthritis in adults. The. Lancet. 375, 846–855 (2010).
- Fangous M-S, Hémon F, Graf Pet al. Bone infections caused by Gemellahaemolysans. Médecine. Mal. Infect. 46, 449–452 (2016).
- Gatibelza ME, Laroye B, Lombard Jet al. Management of a Ruptured Infected Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and a Spondylodiscitis Due to Gemellahaemolysans. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 23, 536.e13-536.e17 (2009).
- Rajagopal TS, Walia M, Wilson HA et al. Gemellahaemolysans spondylodiscitis. J. Bone. Joint. Surg. Br. 94-B, 825–828 (2012).
- Eggelmeijer F, Petit P, Dijkmans Bac. Total Knee Arthroplasty Infection Due To Gemella Haemolysans. Rheumatology. 31, 67–69 (1992).
- Hayashi T, Uchiumi H, Yanagisawa Ket al. Recurrent Gemellahaemolysans Meningitis in a Patient with Osteomyelitis of the Clivus. Intern. Med. 52, 2145–2147 (2013).