Research Article - Journal of Pharmaceutical Toxicology (2023) Volume 6, Issue 3
The Growing Concern: Rising Drug Abuse Rates and the Urgent Need for Action
Ioan Mayer*
Department of Pharmacology, University of Oradea, Romania
- *Corresponding Author:
- Ioan Mayer
Department of Pharmacology, University of Oradea, Romania
E-mail: ioan.mayer@yahoo.com
Abstract
In recent years, the world has witnessed a disconcerting surge in drug abuse cases, posing a significant challenge to public health and society as a whole. From opioids and stimulants to synthetic substances, the global drug landscape has become increasingly complex, necessitating immediate attention and comprehensive strategies to tackle this pressing issue. This article delves into the current state of drug abuse, explores the factors contributing to its escalation, and highlights the urgent need for concerted action to mitigate it’s devastating consequences. Over the past decade, drug abuse rates have experienced a troubling upswing, both in developed and developing countries alike. Statistics paint a grim picture, with an exponential increase in substance use disorders, drug-related hospitalizations, and overdose fatalities. This section presents the latest data, shedding light on the magnitude of the problem and its multifaceted impact on individuals, families, and communities. Understanding the underlying factors that drive drug abuse is crucial for formulating effective prevention and intervention strategies.
Keywords
Mucilage • Pharmaceutical excipients • Tablets • Physicochemical characterization
Introduction
Efficient policies and legislation play a pivotal role in addressing drug abuse. This section analyzes existing drug policies, highlighting both their strengths and limitations. It emphasizes the importance of evidence-based approaches, harm reduction strategies, and interdisciplinary collaborations to combat drug abuse effectively. Additionally, it explores the need for policy reforms to prioritize prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation over punitive measures. In the fight against drug abuse, innovative approaches and interventions are emerging as potential game-changers. This part showcases promising initiatives, such as community-based programs, technology-driven interventions, and alternative treatment modalities. It examines how these novel approaches can enhance prevention efforts, early intervention, and long-term recovery, fostering a comprehensive and compassionate response to drug abuse. This segment explores a range of determinants, including social, economic, and environmental factors, as well as psychological and genetic vulnerabilities. It also examines the influence of factors such as poverty, unemployment, mental health disorders, and peer pressure on initiating and perpetuating substance abuse patterns [1-3].
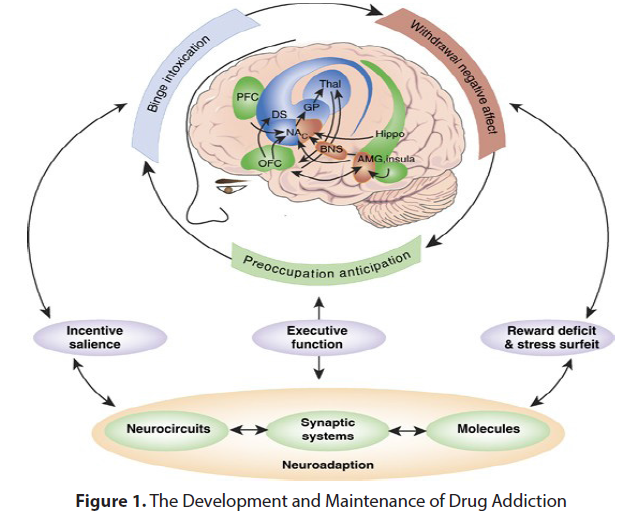
Education and awareness campaigns are vital in curbing drug abuse and reducing its social impact. This segment explores the significance of robust educational programs targeting schools, colleges, and communities, equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills to make informed decisions regarding drug use. It also underscores the importance of reducing stigma surrounding addiction, promoting empathy, and fostering a supportive environment for those seeking help. Addressing the drug abuse crisis necessitates a collective effort from governments, healthcare professionals, communities, and individuals. This final section emphasizes the urgent need for collaboration, resource allocation, and coordinated action to tackle this complex issue comprehensively. By working together, we can create a future where drug abuse is effectively prevented, treated, and ultimately eradicated, ensuring the well-being and prosperity of generations to come (Figure 1).
Material and Methods
As drug abuse rates continue to rise at an alarming pace, it is imperative that we confront this crisis head-on. By acknowledging the severity of the problem, understanding its root causes, implementing evidence-based policies, and fostering education and awareness, we can forge a path towards a drug-free society. Together, we must strive to protect individuals, families, and communities from the devastating consequences of drug abuse and pave the way for a healthier, safer future. The world of drug use and abuse is an ever-evolving landscape, with new trends and patterns constantly emerging. In this article, we delve into some of the latest developments and shifts in drug use, shedding light on the implications and potential consequences of these emerging trends.
In recent years, the illicit market has witnessed a surge in the availability and use of synthetic opioids. These potent substances, often manufactured in clandestine laboratories, present a grave danger to individuals and communities. We explore the reasons behind this alarming trend, the risks associated with synthetic opioids, and the urgent need for comprehensive intervention strategies. Micro dosing, the practice of consuming small, sub-perceptual amounts of psychedelic substances like LSD or psilocybin mushrooms, has gained significant attention in both scientific and popular circles. We delve into the reported benefits of micro dosing, such as increased creativity and improved mood, as well as the ongoing debate surrounding its efficacy, legality, and potential risks.
Results
As more countries and states move towards legalizing cannabis for medicinal and/or recreational use, a unique set of challenges and opportunities arise. We examine the effects of cannabis legalization on public health, crime rates, taxation, and regulatory frameworks, drawing insights from jurisdictions that have already implemented such policies. The advent of the dark web has revolutionized the drug trade, providing a platform for anonymous transactions and global distribution. We explore the inner workings of these hidden online marketplaces, the challenges faced by law enforcement agencies, and the potential consequences for public health and safety.
Novel psychoactive substances (NPS), commonly known as “legal highs,” continue to pose a significant threat to public health. These synthetic compounds, often designed to mimic the effects of illicit drugs, circumvent legal frameworks and pose challenges for legislation and enforcement. We discuss the risks associated with NPS, the difficulties in regulating them, and the importance of public awareness campaigns. The world of drug use is a complex and ever-changing realm, requiring ongoing research, proactive policies, and public education to address emerging trends effectively. By staying informed about the latest developments in substance abuse, society can better understand the risks, develop targeted interventions, and ultimately strive towards a healthier and safer future for all.
Discussion
The pharmaceutical industry plays a crucial role in advancing medical treatments and improving global health. However, the development and regulation of drugs are complex processes that require careful consideration of various factors, including innovation, efficacy, and patient safety. This article explores the challenges and considerations involved in drug regulation, highlighting the need for a delicate balance between promoting innovation and ensuring public health.
Drug regulation serves as a critical safeguard for public health by evaluating the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products. Rigorous testing and regulatory processes are designed to ensure that drugs are both effective in treating the intended conditions and safe for consumption. Regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe, and other national agencies worldwide, play a vital role in assessing and approving drugs for market availability. While drug regulation aims to protect public health, it is equally important to foster innovation in the pharmaceutical industry. Innovation drives the development of novel treatments, enhances patient outcomes, and addresses unmet medical needs. Streamlining regulatory processes, offering incentives for research and development, and encouraging collaboration between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies can facilitate the advancement of innovative drugs [4,5].
The safety of patients is paramount in drug regulation. Adverse effects, drug interactions, and long-term risks must be carefully assessed before a drug is approved for widespread use. Postmarketing surveillance and pharmacovigilance systems play a vital role in monitoring the safety and effectiveness of drugs once they are on the market. Timely reporting of adverse events and continuous evaluation of safety data help identify and manage potential risks. The landscape of drug regulation is dynamic and continuously evolving. Rapid advancements in technology, such as gene therapy and personalized medicine, present new challenges in evaluating the safety and efficacy of innovative treatments. Regulatory agencies need to adapt and develop new frameworks to assess these emerging therapies effectively. Additionally, the globalization of drug development and the rise of the digital health industry require international collaboration and harmonization of regulatory standards [6,7].
Drug regulation serves as a critical foundation for public health by ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. Striking a balance between fostering innovation and safeguarding patient welfare is essential. Continuous dialogue and collaboration among regulatory bodies, industry stakeholders, healthcare professionals, and patient advocacy groups are key to addressing the challenges and evolving landscape of drug regulation. By adapting to new technologies and embracing emerging trends, regulators can effectively promote innovation while maintaining rigorous standards to protect public health. In recent years, the debate surrounding drug legalization has gained momentum and ignited discussions worldwide. Advocates argue that legalizing certain drugs could have positive social and economic outcomes, while opponents express concerns about potential risks and consequences. This article delves into the complexities of drug legalization, examining both the potential benefits and challenges associated with this contentious issue [8,9].
As societal attitudes toward drug use evolve, there has been a shift away from the traditional “war on drugs” approach. This section explores how countries and communities are reevaluating their drug policies, considering harm reduction strategies, and exploring alternative approaches such as decriminalization and regulated markets. Legalizing drugs could open up new economic opportunities. This section examines the potential for revenue generation through taxation and regulation, drawing examples from regions that have implemented drug legalization models. It also explores the potential for job creation and economic growth in related industries. Drug legalization brings both potential benefits and risks to public health. This section discusses the impact on substance abuse patterns, addiction rates, and the availability of treatment options. It also highlights the importance of implementing robust public health campaigns and harm reduction measures in conjunction with legalization efforts.
The criminalization of drug use and possession has led to overburdened criminal justice systems and disproportionately affects marginalized communities. This section explores how drug legalization could alleviate the strain on the legal system, reduce incarceration rates, and redirect resources toward more effective law enforcement strategies. Various countries have implemented different approaches to drug legalization, providing valuable lessons for policymakers and researchers. This section examines case studies from countries like Portugal, Uruguay, and Canada, analyzing their experiences and the outcomes of their drug policy reforms [10-12].
Despite the potential benefits, drug legalization is not without its challenges. This section explores the contentious issues surrounding drug legalization, such as regulation, public perception, addiction treatment availability, and the risk of increased drug-related harm. It highlights the importance of evidence-based policies and ongoing evaluation to address these challenges effectively. As the discourse around drug legalization continues to evolve, it is essential to consider the multifaceted nature of this complex issue. While proponents argue for the potential benefits, it is crucial to navigate the challenges responsibly and prioritize public health and safety. By examining the economic, public health, and criminal justice implications, policymakers can make informed decisions to shape drug policies that are effective, equitable, and compassionate.
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in the potential therapeutic benefits of psychedelic substances for mental health treatment. Research on psychedelic-assisted therapy, which combines the use of psychedelics with psychotherapy, has shown promising results in treating conditions such as depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and addiction. This article explores the growing body of evidence surrounding psychedelicassisted therapy and its potential to revolutionize the field of mental health treatment.
Psychedelic substances, such as psilocybin (found in magic mushrooms) and MDMA (commonly known as ecstasy), have a long history of traditional use in indigenous cultures. However, their recreational abuse and association with counterculture movements in the 1960s led to their criminalization and stigmatization. It was not until recent years that researchers began reexamining their potential therapeutic applications. With the loosening of legal restrictions on psychedelic research, scientists have conducted a series of groundbreaking studies, aiming to unravel the therapeutic potential of these substances. Clinical trials involving psychedelic-assisted therapy have demonstrated significant improvements in various mental health conditions. For example, studies have shown that MDMA-assisted therapy can lead to remarkable reductions in symptoms of PTSD, while psilocybin-assisted therapy has shown promise in alleviating treatment-resistant depression [13-15].
Researchers have been studying the mechanisms by which psychedelic substances exert their therapeutic effects. It is believed that these substances work by modulating neural circuits related to emotion, memory, and self-identity. They can induce profound alterations in consciousness, allowing patients to explore their thoughts, emotions, and traumatic experiences in a safe and supported therapeutic setting. This heightened state of consciousness, combined with psychotherapy, enables individuals to gain new insights, process trauma, and foster personal growth.
While the results of psychedelic-assisted therapy have been promising, there are still many challenges to overcome. Safety concerns, legal barriers, and the need for specialized training in administering these therapies are among the key obstacles. However, as public perception shifts and research continues, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will evolve, paving the way for wider access to these treatments. Future research endeavors will focus on optimizing therapeutic protocols, exploring different psychedelic substances, and conducting large-scale trials to establish the long-term safety and efficacy of psychedelic-assisted therapy. The renaissance of psychedelic-assisted therapy has the potential to transform the landscape of mental health treatment. By challenging conventional approaches and offering new avenues for healing, these therapies hold promise for individuals who have not responded to traditional treatments. Although further research is needed, the resurgence of interest in psychedelic-assisted therapy signifies a paradigm shift in the field of mental health, offering hope for a brighter future in the treatment of various psychiatric conditions [16-18].
In recent years, the landscape of drug use has been evolving, presenting society with new challenges and the need for innovative solutions. This article aims to shed light on the emerging trends in drug use, highlighting their implications and exploring potential strategies to address this pressing issue. By understanding these developments, we can work towards more effective prevention, treatment, and harm reduction approaches.
With the advent of the internet and the rise of the dark web, synthetic drugs have become increasingly accessible. These chemically engineered substances, such as synthetic cannabinoids and novel psychoactive substances, pose unique challenges due to their constantly evolving nature and ability to bypass traditional drug regulations. This section explores the impact of synthetic drugs on public health, the challenges they present to law enforcement, and the importance of international cooperation in combating their proliferation. The opioid crisis continues to ravage community’s worldwide, demanding urgent attention. This section delves into the factors contributing to the opioid epidemic, including overprescribing, the spread of illicitly manufactured fentanyl, and the complex relationship between prescription opioids and heroin use. Moreover, it examines promising interventions, such as harm reduction strategies, medication-assisted treatment, and the importance of DE stigmatizing addiction [19,20].
Conclusion
In the face of emerging drug trends, innovative approaches are essential. This section discusses the potential of technology, such as artificial intelligence and data analytics, in detecting and responding to drug-related issues. Furthermore, it explores progressive policy initiatives, such as harm reduction programs, decriminalization, and alternative sentencing, as means to reduce drug-related harm and improve public safety. As drug use patterns continue to evolve, society must adapt its approach to prevention, treatment, and policy. By acknowledging and understanding emerging drug trends, we can develop evidencebased interventions that effectively address the challenges at hand. It is crucial to foster collaboration among researchers, policymakers, healthcare professionals, and communities to ensure a comprehensive and compassionate response to the complex issues surrounding drug use in the modern world.
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in the therapeutic potential of psychedelics, such as psilocybin and MDMA. This section examines the growing body of research supporting their efficacy in treating mental health conditions, including depression, PTSD, and addiction. It also discusses the regulatory challenges surrounding psychedelicassisted therapy and the importance of integrating these substances into evidencebased treatment models. With an increasing number of jurisdictions legalizing cannabis for medicinal and recreational purposes, this section explores the potential benefits and risks associated with this shift. It examines the impact of cannabis legalization on public health, youth consumption, criminal justice, and the economy. Additionally, it highlights the importance of responsible regulation, education, and addressing disparities in the enforcement of drug laws.
Acknowledgement
None
Conflict of Interest
None
References
- Saraswat A. Topical corticosteroid use in children: Adverse effects and how to minimize them. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 76, 225–228 (2010).
- Beggs S. Paediatric analgesia. Aust Prescr. 31, 63–65 (2008).
- Rossi M, Giorgi G. Domperidone and long QT syndrome. Curr Drug Saf. , 5, 257–262 (2010).
- Kosek M, Bern C, Guerrant RL. The global burden of diarrhoeal disease, as estimated from studies published between 1992 and 2000. Bull World Health Organ. 81, 197–204(2003).
- Alam N, Najam R. Effect of repeated oral therapeutic doses of methylphenidate on food intake and growth rate in rats. Pak J Pharm Sci. 28 9–13(2015).
- Ryan C, Ross S, Davey P et al. Prevalence and causes of prescribing errors: The PRescribing Outcomes for Trainee Doctors Engaged in Clinical Training (PROTECT) study. PLoS ONE. 9, 69-143 (2006).
- Patrick DM, Marra F, Hutchinson J et al. Per capita antibiotic consumption: How does a North American jurisdiction compare with Europe? Clin Infect Dis. 39, 11-17 (2004).
- Li WC. Occurrence, sources, and fate of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environment and soil. Environ Pollute. 187, 193-201 (2014).
- Heberer T. Occurrence, fate, and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment:A review of recent research data. Toxicol Lett. 131, 5-17 (2002).
- Banci L, Ciofi-Baffoni S, Tien M Lignin et al. Peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of phenolic lignin oligomers. Biochemistry. 38, 3205-3210 (1999).
- Berthe-Aucejo A, Nguyen PKH, Angoulvant F et al. Retrospective study of irrational prescribing in French paediatric hospital: Prevalence of inappropriate prescription detected by Pediatrics: Omission of Prescription and Inappropriate prescription (POPI) in the emergency unit and in the ambulatory setting. BMJ Open. 9, 45-66(2015).
- Al Balushi KA, Al-Sawafi F, Al-Ghafri F et al. Drug utilization pattern in an Omani pediatric population. J. Basic Clin Pharm. 4, 68–72(2014).
- Al-Badri A. Almuqbali J, Al-Rahbi K et al. A Study of the Paediatric Prescriptions at the Tertiary Care Hospital in Oman. J Pharmaceut Res. 5, 17-56(2020)
- Al-Maqbali, Haridass S, Hassali M et al. Analysis of Pediatric Outpatient Prescriptions in a Polyclinic of Oman. Glob. J Med Res. 19, 2249–4618(2019).
- Bakaki PM, Horace A, Dawson N et al. Defining pediatric polypharmacy: A scoping review. PLoS ONE , 13, 56-99(2018).
- Lemeshow S, Hosmer DW. A review of goodness of fit statistics for use in the development of logistic regression models. Am J Epidemiol. 115, 92–106(1982).
- Wallace E, McDowell R, Bennett K et al. Impact of Potentially Inappropriate Prescribing on Adverse Drug Events, Health Related Quality of Life and Emergency Hospital Attendance in Older People Attending General Practice: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 72, 271–277(2017)
- Cahir C, Moriarty F, Teljeur C et al. Potentially inappropriate prescribing and vulnerability and hospitalization in older community-dwelling patients. Ann Pharmacother. 48, 1546–1554(2018).
- Cullinan S, O’Mahony D, Fleming A et al. A meta-synthesis of potentially inappropriate prescribing in older patients. Drugs Aging.31, 631–638(2014).
- Liew TM, Lee CS, Goh Shawn KL et al. Potentially Inappropriate Prescribing Among Older Persons: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Ann Fam Med. 17, 257–266(2019).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross ref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref