Clinical images - Imaging in Medicine (2020) Volume 12, Issue 4
Pagets disease of the breast
Iyda El faqyr1*, Imane Yafi2, Yassine Benchamkha2, Said Amal1
- Corresponding Author:
- Iyda El faqyrDermatology Department, Mohammed VI University Hospital, Marrakech, Morocco Email: iydaelfaqyr@gmail.com
Abstract
Keywords
Mammary paget’s disease ■ Breast cancer ■ Dermoscopy ■ Breast MRI
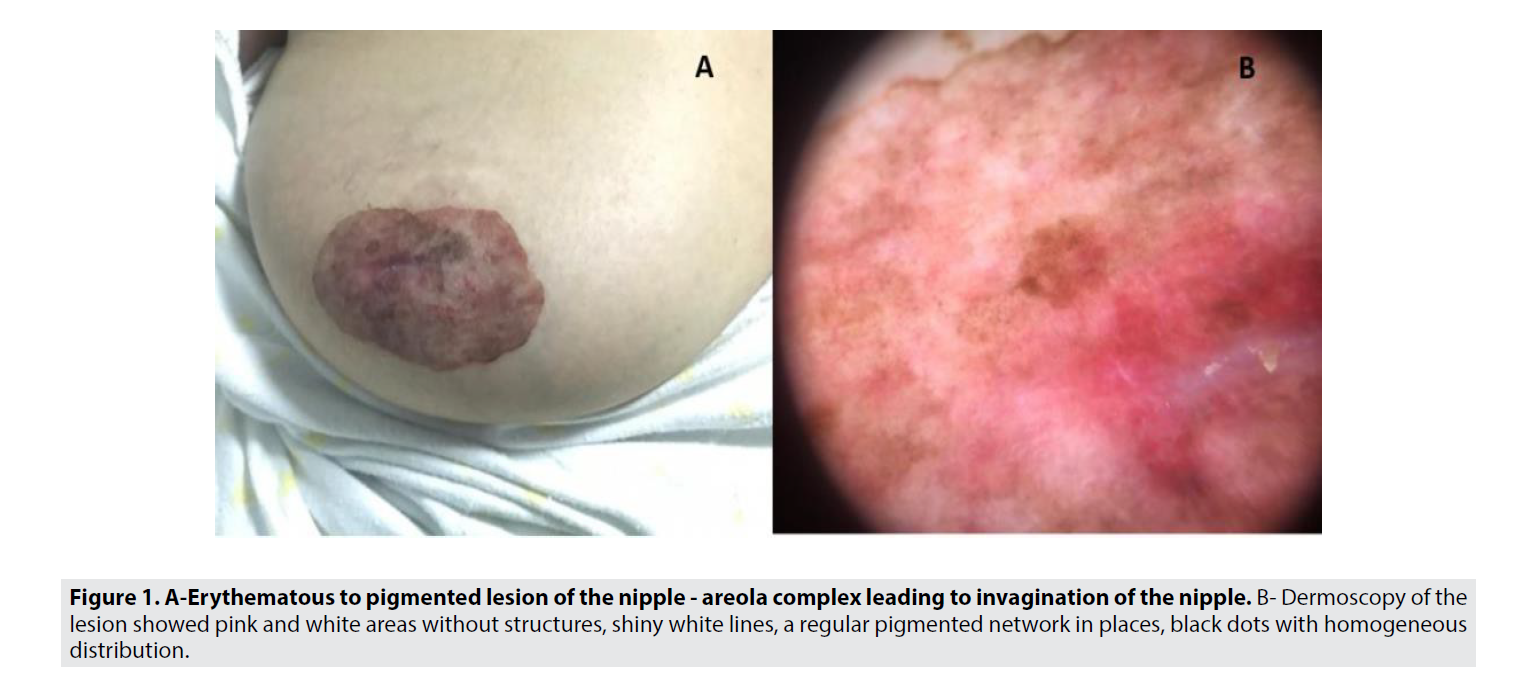
A 62yr old female presented to our dermatology department for a lesion of the right nipple–areola complex of three years duration. The lesion had been growing gradually. Clinical examination showed a well demarcated, erythematous to pigmented plaque of 7cm × 5 cm, leading to invagination of the nipple (FIGURE 1A). There was no discharge, erosion or bleeding. There was no breast lump or enlarged axillary lymph nodes.
Dermoscopy of the lesion showed pink and white areas without structures, shiny white lines, a regular pigmented network in places, black dots with homogeneous distribution (FIGURE 1B). Histology revealed intraepidermal proliferation of atypical cells with large pleomorphic nuclei and abundant cytoplasm, compatible with Paget cells.
Mammography, ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging had shown no signs of breast cancer. The patient had undergone tumor excision with 1 cm lesion margin. Histology of excised specimen confirmed the intraepidermal nature of the proliferation. We decided no further treatment. At one year follow up, the patient is still disease free. Mammary Paget’s disease is rare and often associated with intraductal cancer. It usually presents as erythematous, eczematoid, moist or crusted lesion, with or without fine scaling. It should be distinguished from erosive adenomatosis of the nipple, Bowen's disease, basal cell carcinoma, psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. Diagnosis is histological. Treatment and prognosis depend on the type of underlying breast cancer. In this case, there was no obvious ductal advancement and no signs of solid tumor in the breast. In a patient with mammary Paget’s disease, we should absolutely rule out underlying breast cancer.