Clinical images - Imaging in Medicine (2020) Volume 12, Issue 2
Aorto-left atrial fistula in native aortic valve endocarditis secondary to Streptococcus mitis
Wen Qian Zheng1*, Muhammed Saad Shaukat1, Hiren Patel2 & Mikhail Torosoff21Department of Internal Medicine, Albany Medical Center, Albany, New York, USA
2Department of Cardiology, Albany Medical Center, Albany, New York, USA
- Corresponding Author:
- Wen Qian Zheng
Department of Internal Medicine
Albany Medical Center
Albany New York, USA
E-mail: zhengw@amc.edu
Abstract
Aorto-cavitary fistulas are rare and serious complications of infectious endocarditis. We present a case of a patient with native bicuspid aortic valve endocarditis secondary to Streptococcus mitis. Intra-operative transesophageal echocardiogram revealed a hemodynamically significant shunt between the aortic root and left atrium via the mitral-aortic inter-vascular fibrosa. Despite initially doing well after aortic valve replacement and fistula repair, he presented back 3 weeks later and rapidly decompensated, eventually succumbing to cardiac arrest. Such cases are often associated with higher rates of acute heart failure and post-operative mortality remains high.
Keywords
aortic valve endocarditis ■ intraoperative transesophageal echocardiogram
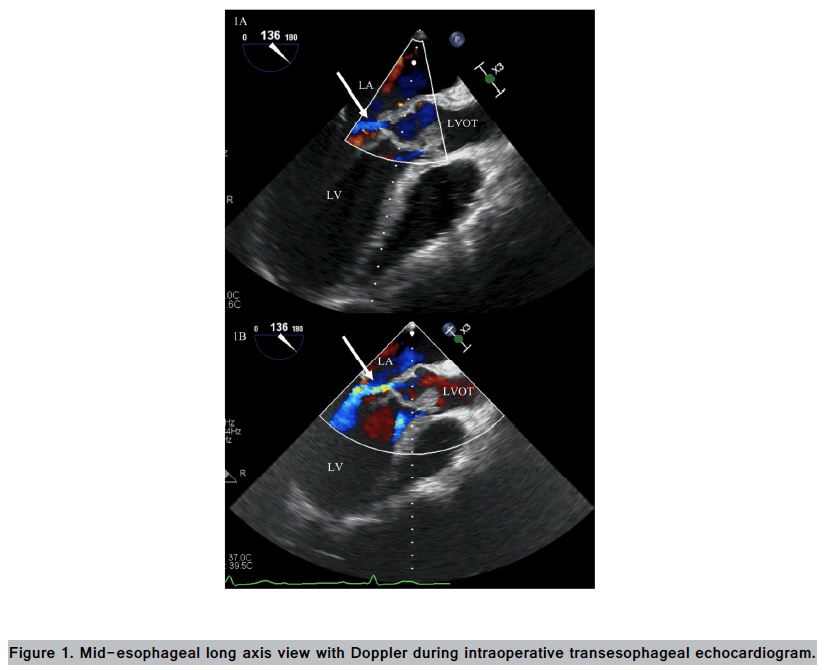
A 44 y old male with history of Lyme carditis presents to an outside hospital with 1 week of fevers, rigors, and progressive dyspnea at rest. He was transferred to our facility for concern of Infective Endocarditis (IE). On admission, patient was hemodynamically stable. Labs significant for leukocytosis of 25.9, lactic acid of 7.33, and troponin-I of 1.22. A few hours later, he suddenly went into cardiac arrest and was successfully resuscitated. Bedside echocardiogram showed severe aortic valve insufficiency with vegetations, concerning for aortic valve rupture. Emergent intra-operative transesophageal echocardiogram revealed a bicuspid aortic valve with acute severe aortic insufficiency and a hemo-dynamically significant fistula between the aortic root and the left atrium during diastole (FIGURE 1). He underwent tissue aortic valve replacement and replacement of the aortomal curtain with intraoperative cultures were positive for Streptococcus mitis. He was eventually discharged with 6 weeks of ceftriaxone. He presented back on post-operative day 18 with fevers and rigors, and was admitted for severe sepsis. Despite aggressive treatment, his rapidly decompensated and ultimately succumbed to cardiac arrest.
Top and bottom panels are consecutive frames taken during diastole. Cardiac chambers labeled andwhite arrow denotes flow between left atrium and aortic root. Aortic vegetation also visible. LA = left atrium, LV = left ventricle, LVOT = left ventricular outflow tract.
Aorto-cavitary fistulas manifest when bacterial invasion spread beyond peri-annular structures in IE [1]. In our patient, there was direct extension of the infection of the aortic valve into the mitral-aortic intervascular fibrosa, leading to perforation into the left atrium and subsequent hemodynamic instability. Such complications occur most commonly in staphylococcus and streptococcus IE, and in patients with bicuspid aortic valves or artificial valves [2]. Despite timely surgical intervention, post-operative mortality remains high in cases of aorto-cavitary fistula. Unfortunately, although initially doing well, the patient ultimately succumbed 3 weeks later. He likely developed increasing bacterial burden after hospital discharge, resulting in acute complications including possible secondary valvular involvement, abscesses, aneurysms, and/or acute heart failure that lead to circulatory collapse.
Author Contributions
WQZ, MMS and HP planned the case report. WQZ and MMS collected the data and drafted the manuscript. HP and MT critically reviewed the final manuscript.
References
- Anguera I, Miro JM, Evangelista A et al. Periannular complications in infective endocarditis involving native aortic valves. Am. J. Cardiol. 98, 1254-1260, (2006).
- Anguera I, Miro JM, Vilacosta I et al. Aortocavitary fistulous tract formation in infective endocarditis: clinical and echocardiographic features of 76 cases and risk factors for mortality. Eur. Heart J. 26, 288-297, (2005).